Distance-time graphs

Acceleration

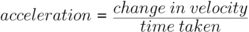

This is when:

- In a distance-time graph, the gradient of the line is equal to the speed of the object. The greater the gradient (and the steeper the line) the faster the object is moving.
- If an object is accelerating or decelerating, its speed can be calculated at any particular time by:
- drawing a tangent to the curve at that time
- measuring the gradient of the tangent
- The gradient of the line is equal to the acceleration of the object.
- The displacement of an object can be calculated from the area under a velocity-time graph.
Acceleration
- Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. It is the amount that velocity changes per unit time.
- The change in velocity can be calculated using the equation:
- change in velocity = final velocity - initial velocity
- The average acceleration of an object can be calculated using the equation:
This is when:
- acceleration (α) is measured in metres per second squared (m/s²)
- change in velocity (∆v) is measured in metres per second (m/s)
- time taken (t) is measured in seconds (s)
- If an object is slowing down, it is decelerating (and its acceleration has a negative value).
- This equation applies to objects in uniform acceleration:
- This is when:
- final velocity (v) is measured in metres per second (m/s)
- initial velocity (u) is measured in metres per second (m/s)
- acceleration (a) is measured in metres per second squared (m/s2)
- displacement (s) is measured in metres (m)
Downloaded from https://qusaistuition.blogspot.com










0 comments:
Post a Comment